Onboarding is a necessary process for all companies that want their employees to thrive and succeed. Their experience will have a direct correlation to their contribution.
Onboarding is defined simply as the process through which new employees adopt the organization’s culture. This process isn’t simply the ability to recite information but it’s knowing how to thrive in the new environment and navigating through unknown territory. The key here is learning to adopt and adapt into the dominant culture.
SO WHY IS ONBOARDING IMPORTANT?
 Studies have revealed that attrition rates tend to be higher for those companies that have not spent time in their onboarding process of new hires. This boils down to loss of revenue since it costs money to hire and train people. Typically it takes between 3-6 months before a new employee is actually able to begin their significant contribution to the organization. During this timeframe they are typically consumers of time, money and energy. When they leave before this milestone, they leave the organization with a deficit. Healthy onboarding solves this dilemma by providing the necessary experience that catapults the new employee to success for themselves and the company.
Studies have revealed that attrition rates tend to be higher for those companies that have not spent time in their onboarding process of new hires. This boils down to loss of revenue since it costs money to hire and train people. Typically it takes between 3-6 months before a new employee is actually able to begin their significant contribution to the organization. During this timeframe they are typically consumers of time, money and energy. When they leave before this milestone, they leave the organization with a deficit. Healthy onboarding solves this dilemma by providing the necessary experience that catapults the new employee to success for themselves and the company.
One of the most critical questions that need to be addressed in any onboarding process is: Why does the company exist? It’s not what the company provides or how it does its work. But why does the company exist that makes it unique from everyone else?
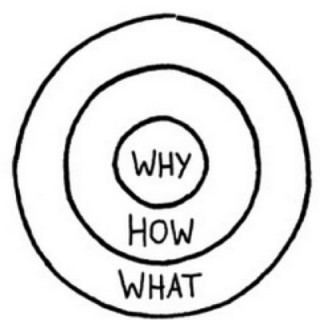
Simon Sinek introduces this concept in “The Golden Circle.” Basically, there are 3 concentric circles that look like the ripples of water when a pebble is dropped into still water. Moving from inside out: at the center is WHY, the next circle is HOW and the final external circle is WHAT.
- WHAT: Every organization on the planet knows WHAT they do. These are the products they sell or the services they offer.
- HOW: Some organizations know HOW they do it. These are the things that make them special or set them apart from their competition.
- WHY: Very few organizations know WHY they do what they do. WHY is not about making money. That’s a result. It’s a purpose–cause or belief. It’s the very reason your organization exists.
The successful organizations understand this concept and live it out. For example, here’s what Apple’s marketing might look like if they did what other companies do:
- What: We make great computers.
- How: They’re beautifully designed, simple to use, and user-friendly.
- Want to buy one?
This is the way Apple actually markets their products:
- Why: In everything we do, we believe in challenging the status quo. We believe in thinking differently.
- How: The way we challenge the status quo is by making our products beautifully designed, simple to use, and user friendly.
- What: We just happen to make great computers.
- Want to buy one?
Starting with why is a lot more convincing, right?
Getting to understand and communicate your WHY?, HOW? and WHAT? Is essential to the success of your company and more importantly to persuade your new employees to also adopt them. It’s during the next 90 days, the onboarding process will be critical for your new employee to learn and adopt the culture of your organization.

THERE ARE THREE CRITICAL FOUNDATIONS FOR ONBOARDING: OBJECTIVES, SKILLS AND VALUES.
Foundational Objectives are needed to create the platform for the employee to launch from. These objectives answer WHY the company exists. What are the vision, mission and functional values of the organization?
A few of the key questions to consider are:
- Why does the company exist?
- How does the team the employee is a part of contribute to this Why?
- How does the employee contribute to the team?
The key channel through which the objectives are achieved is to create an orientation process that creates the opportunity for the new hire to dialogue and learn through the natural relationships with others around them. Creating intentional relationships with role models who can come alongside the new employee are critical. Picking your top performers in the company is a helpful metric to select role models. They would be those that are the keepers of your core values and understand the WHY behind your company’s existence.
Foundational Skills
Core competencies exist for any organization. These are usually found in the SOPs, employee handbook, etc. All of these acquired skills will take time for the new hire to ingest and then to interpret into their application in their work. The relationship with the role model will help them to navigate through all the information available.
One of the key essentials in this process is a mindset that the new hire needs to adopt: “maintaining a learning posture” is key to the new hire’s success. If they are proud and not teachable, they will not adopt the organizational culture.
Foundational Values
Values are the non-negotiables of any culture. They create the framework through which decisions and behaviors erupt. Who are the keepers of the values in a community? Simply put, it is those who are the influencers. It’s the people that the followers look toward for leadership and inspiration.
Pairing the new employee with the key influencers is a strategic move to best assimilate them into your organization. You will probably end up with a new hire learning much quicker if they are paired with someone that is entrusted with the values of the company.
If you’re the manager, ask yourself who are the employees that you trust. Who understands why we exist and express the values of who we represent as a culture? People follow people. This is why values are not necessarily taught via information transfer but rather caught through modeling after those that they are inspired by.
Your organization will succeed in creating effective and productive personnel through your successful onboarding process. Just remember to create the Key Foundational Objectives, Skills and Values.

